Your skin’s cracking, your throat feels like sandpaper, and that static shock from the doorknob just launched you across the room. Winter’s here, and your home’s humidity has plummeted to desert levels. An evaporative humidifier might be your salvation—but before you buy one, understanding how an evaporative humidifier works will help you choose the right model and avoid costly mistakes.
Unlike steam vaporizers that boil water or ultrasonic units that create mist clouds, evaporative humidifiers work with nature, not against it. They simply accelerate the same process that dries your clothes on a windy day. Let’s dive into the elegant physics that make these devices so effective and safe.
The Physics Behind Evaporative Humidifier Operation: Capillary Action + Airflow
Two simple forces power every evaporative humidifier: capillary action and air movement. No pumps, no heating elements, no complex electronics—just physics doing what it does best.
Capillary action pulls water upward through the wick like ink through blotting paper. This creates a continuously moistened surface without any mechanical assistance. The fan assembly then pushes dry room air through this saturated wick, forcing rapid evaporation. This combination transforms a small water reservoir (0.5-6 liters) into 250-800 milliliters of airborne moisture per hour.
The beauty lies in self-regulation. As your room humidity rises, evaporation naturally slows—preventing the over-humidification that plagues other technologies. When relative humidity reaches 50%, output typically drops by 30% compared to operation at 30% humidity. This natural feedback loop means you won’t wake up to condensation on your windows like you might with other humidifier types.
Why Evaporative Humidifiers Don’t Create Visible Mist
Unlike ultrasonic models that produce a visible cool mist, evaporative humidifiers work invisibly. The water molecules become fully integrated into the air stream through true evaporation, not atomization. This eliminates the “white dust” problem common with ultrasonic units when using hard water, making evaporative models safer for people with respiratory conditions.
Water Reservoir Design: Capacity, Materials & Safety Mechanisms
The reservoir isn’t just a bucket—it’s a precision-engineered component that determines runtime, safety, and maintenance frequency.
Capacity ranges span from compact 0.5-liter desktop units to console models holding 6 liters. Furnace-mounted systems can store 10-20 liters for whole-house coverage. Most residential units use BPA-free ABS plastic for safety, while premium models feature antimicrobial coatings that inhibit bacterial growth for up to 30 days.
Critical safety features you should look for:
– Safety float switches that automatically shut off the fan when water drops below 5mm
– Top-fill designs with flip lids instead of bottom-fill tanks for easier refills
– Molded handles to prevent slips during refilling
– Clear MAX fill lines to avoid overflow
Pro Tip: When shopping, prioritize models with wide reservoir openings that allow you to easily insert your hand for cleaning. Narrow openings make proper maintenance nearly impossible.
Wick Technology Deep Dive: Materials, Saturation Rates & Lifespan

The wick serves as both water transport system and evaporation surface—making it the heart of humidifier performance.
Material types dramatically affect both performance and maintenance:
– Cellulose paper: Budget-friendly but requires replacement every 2-4 weeks
– Polyurethane foam: Washable and lasts 3-6 months with minimal mineral buildup
– Aluminum mesh polymer: Premium option lasting 12-24 months in high-end units
Saturation speed determines effectiveness—quality wicks absorb 300+ milliliters within 60 seconds to maintain 500 mL/hour output. Antimicrobial treatments using silver-ion or triclosan coatings prevent mold growth, though effectiveness diminishes after 30 days of continuous use.
How to Tell When Your Wick Needs Replacement
Check your wick weekly for these warning signs:
– Stiffness or loss of flexibility
– Discoloration (yellowing or dark spots)
– Musty odor even after cleaning
– Reduced moisture output despite full water tank
Fan Performance: Noise Levels, Airflow Ratings & Motor Types
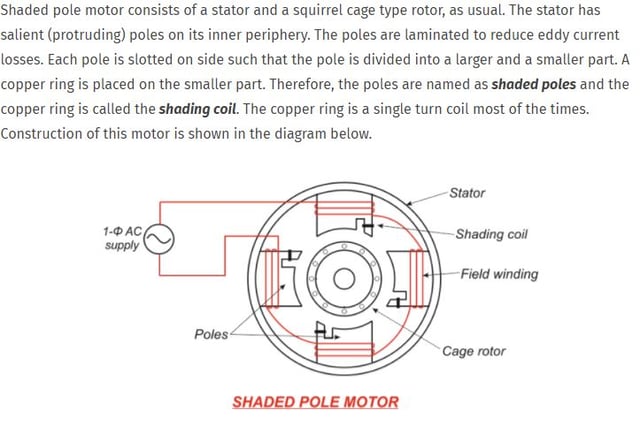
The fan transforms passive evaporation into a moisture-delivering powerhouse, but not all fans are created equal.
Motor types directly impact noise and efficiency:
– Shaded-pole AC: Fixed speed, low cost, consistent but louder
– DC brushless: 3-5 speed settings, whisper-quiet operation
– ECM motors: Variable speed control for whole-house systems
Airflow ratings determine coverage area:
– Personal units: 15-25 CFM for 100-200 sq ft
– Bedroom models: 60-90 CFM for 300-500 sq ft
– Console units: 120-200 CFM for 500-1,200 sq ft
Noise levels range from 35-40 dB(A) on low (library quiet) to 45-55 dB(A) on high (conversation level). Safety grilles prevent curious fingers while allowing easy filter access.
5-Step Evaporative Humidifier Operation Cycle Explained
Understanding the complete cycle helps troubleshoot issues and optimize performance.
Phase 1: Saturation – Water moves through the wick via capillary action until fully saturated. Excess water drips back into the reservoir, creating a closed-loop system.
Phase 2: Air Intake – The fan pulls dry room air through side or bottom intake grilles, creating negative pressure that draws air toward the wick.
Phase 3: Evaporation – Dry air passes through the saturated wick. Water molecules evaporate, absorbing 2,260 kJ of heat per liter—a process that naturally cools the outgoing air by 2-4°F.
Phase 4: Distribution – Moistened air exits through top louvers, achieving 40-60% relative humidity in 15-30 minutes for rooms up to 500 square feet.
Phase 5: Self-Regulation – As humidity rises, evaporation naturally decreases, providing built-in protection against over-humidification.
Performance Metrics That Matter: Output, Coverage & Efficiency Data
| Specification | Typical Range | What It Means for You |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Output | 250-800 mL/h | 300-500 mL/h ideal for most bedrooms |
| Coverage Area | 250-1,200 sq ft | Match to room size for efficient operation |
| Power Draw | 20-60W | Costs pennies per day even on high |
| Tank Runtime | 8-24 hours | Check daily for bedroom use |
| Filter Life | 2-6 months | Replace quarterly with average tap water |
| Noise Level | 35-55 dB(A) | Low speeds perfect for sleeping |
Output efficiency of 10-15 grams of water per watt-hour makes these units incredibly energy-efficient compared to steam alternatives. For perspective, running a 40W evaporative humidifier for 8 hours costs less than 3 cents in electricity.
Critical Evaporative Humidifier Maintenance Schedule (Daily to Seasonal)
Proper maintenance prevents the “white dust” and musty odors that plague poorly maintained units.
Daily: Empty and rinse the reservoir—especially if the unit sits idle for over 12 hours. This 30-second habit prevents bacterial growth that causes sick-building syndrome.
Weekly: Deep clean with a 1:3 white vinegar solution for 20 minutes to dissolve mineral deposits. Check wick condition—replace if stiff, discolored, or odorous.
Monthly: Replace wicks (cellulose) or clean washable types (foam/aluminum). Vacuum fan blades to maintain airflow and efficiency.
End-of-season: Run dry until automatic shutoff, then store wicks separately. Sterilize the reservoir with 70% isopropyl alcohol before storage.
Diagnosing 5 Common Evaporative Humidifier Problems in Minutes
Quick diagnosis saves time and prevents unnecessary replacements.
No humidity increase typically indicates a dry, clogged, or improperly seated wick. Re-soak or replace the wick, ensuring correct orientation in the housing.
White dust accumulation signals hard water usage. Switch to distilled water or install a demineralization cartridge to eliminate mineral particles.
Musty odors indicate bacterial growth. Replace the wick immediately and disinfect the reservoir with 1:10 bleach solution, followed by thorough rinsing.
Fan runs without airflow suggests dust buildup on blades. Gentle vacuuming or wiping restores proper operation.
Water pooling usually results from overfilling or hairline cracks in the reservoir. Always fill to the MAX line and inspect seams regularly.
Optimal Placement Strategies for Bedrooms, Nurseries & Sensitive Areas
Location dramatically affects performance and safety.
Bedrooms: Position 2-3 feet from the bed on a hard surface. Choose DC motor models for whisper-quiet operation under 40 dB(A).
Living areas: Center placement on hard surfaces maximizes circulation. Avoid corners where airflow becomes restricted.
Nurseries: Mount on high shelves out of reach. Prioritize antimicrobial filters and commit to daily water changes.
Musical instrument storage: Target 45% RH to prevent wood cracking in guitars and pianos. Position near instruments but away from heating vents.
Server rooms: Secure mounting prevents tipping. Install RH alarms at 55% to prevent condensation damage to electronics.
Evaporative humidifiers work by leveraging simple physics—capillary action and air movement—to safely and efficiently add moisture to your home. Unlike other technologies, they naturally prevent over-humidification while providing quiet, energy-efficient operation. Choose the right size for your space, maintain it properly, and you’ll transform your home from a static-charged desert into a comfortable, healthy environment that protects both your family and your belongings.
Next steps: Match your room size to the moisture output recommendations, factor in your local water hardness for filter life expectations, and select a model with appropriate noise levels for your primary use case. Remember that understanding how does an evaporative humidifier work gives you the knowledge to maximize performance while minimizing maintenance headaches.