Are you concerned your air purifier might be emitting ozone, a potentially harmful gas? It’s a valid worry, as some air purifiers, particularly older models or those using certain technologies, can produce ozone as a byproduct. While ozone can be effective at eliminating odors and pollutants, excessive exposure can cause respiratory issues. This guide will help you quickly identify if your air purifier is producing ozone and provide comprehensive solutions to mitigate the risk.
This article goes beyond simply identifying ozone production. We’ll cover how different air purifier technologies relate to ozone emissions, how to test for ozone, what to do if your purifier is emitting it, and how to choose an ozone-free air purifier in the future. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge to ensure your air purifier is improving your air quality safely and effectively.
Understanding Ozone and Air Purifiers
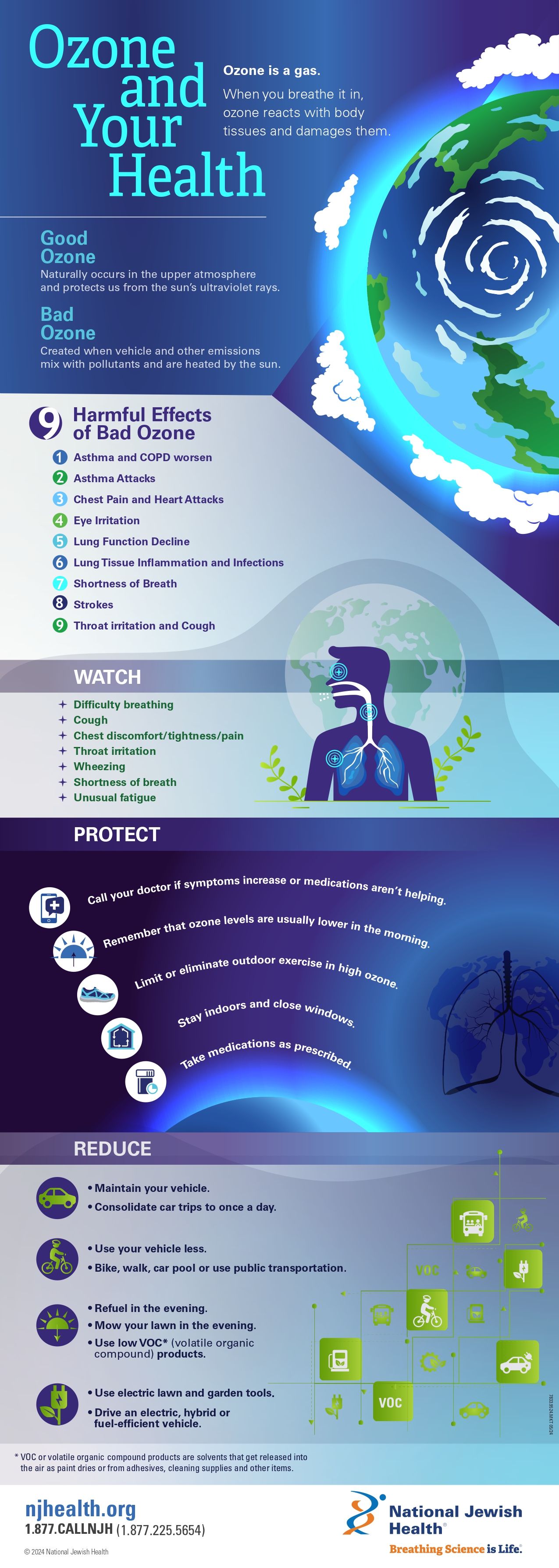
What is Ozone and Why is it Harmful?
Ozone (O3) is a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. While ozone in the upper atmosphere protects us from harmful UV radiation, at ground level, it’s a pollutant. Even low concentrations can irritate the lungs, causing coughing, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Prolonged exposure can worsen chronic respiratory diseases like asthma.
Air Purifier Technologies and Ozone Production

Not all air purifiers produce ozone, but some technologies are more prone to it than others:
- Ionic Air Purifiers: These release negative ions into the air, which attach to pollutants, making them heavier and causing them to fall to the ground. Some ionic purifiers intentionally generate ozone as a supplemental cleaning method.
- UV-C Light Air Purifiers: UV-C light can break down pollutants, but in the presence of oxygen, it can also create ozone. The amount of ozone produced depends on the wavelength of the UV-C light and the design of the purifier.
- Electrostatic Precipitators: These use an electrical charge to trap particles. They can generate ozone as a byproduct of the ionization process.
- HEPA Filter Air Purifiers: Generally, HEPA filters themselves do not produce ozone. However, if combined with other technologies like UV-C or ionizers, the overall unit can generate ozone.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Carbon filters don’t produce ozone; they absorb it, and other odors and gases.
How to Tell if Your Air Purifier is Emitting Ozone
Recognizing the Signs
Ozone has a distinct, sharp odor, often described as similar to chlorine. However, relying on smell alone isn’t reliable, as our ability to detect ozone diminishes with prolonged exposure. Other signs include:
- Watery Eyes and Throat Irritation: If you experience these symptoms while the air purifier is running, it could be a sign of ozone.
- Headaches or Nausea: Ozone exposure can trigger headaches and nausea in some individuals.
- A Static Feeling: Ozone generation can create a noticeable static charge in the air.
Testing for Ozone
There are several ways to test for ozone:
- Ozone Test Strips: These are readily available online and change color in the presence of ozone. They’re a quick and inexpensive way to get a general indication, but aren’t highly accurate.
- Ozone Monitors: These devices provide a digital readout of ozone concentration in parts per million (ppm). They are more expensive than test strips but offer a more precise measurement. Look for monitors specifically designed for indoor air quality.
- Professional Testing: For the most accurate assessment, hire a professional indoor air quality testing service.
What to Do If Your Air Purifier is Producing Ozone

Immediate Steps
- Turn Off the Purifier: Immediately stop using the air purifier if you suspect it’s emitting ozone.
- Ventilate the Room: Open windows and doors to increase airflow and reduce ozone concentration.
- Monitor Your Symptoms: If you’re experiencing any health effects, consult a doctor.
Long-Term Solutions
- Disable Ozone-Generating Features: Many air purifiers with ionizers or ozone generators have a switch to disable these features. Consult your user manual.
- Replace the Filter: A dirty or clogged filter can sometimes contribute to increased ozone production.
- Contact the Manufacturer: If you can’t disable the ozone-generating features or the problem persists, contact the manufacturer for support or a replacement.
- Consider a Replacement: If your air purifier consistently produces ozone even after troubleshooting, it may be time to replace it with an ozone-free model.
Pro Tips for Ozone-Free Air Purification
- Choose HEPA Filter Purifiers: Prioritize air purifiers that use only HEPA filters and activated carbon filters.
- Look for CARB Certification: The California Air Resources Board (CARB) certifies air purifiers that meet strict ozone emission standards. Look for this certification when purchasing.
- Read Reviews Carefully: Pay attention to user reviews that mention ozone odor or health concerns.
- Avoid “Ozone Generators” Marketed as Air Purifiers: These devices intentionally generate high levels of ozone and are not recommended for use in occupied spaces.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly clean or replace filters as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance and minimize potential ozone production.
Professional Help Section
If you suspect significant ozone contamination or are experiencing persistent health issues, consult a professional indoor air quality specialist. They can conduct thorough testing and recommend appropriate remediation measures.
Typical Cost Ranges:
- Indoor Air Quality Testing: $200 – $800 (depending on the scope of testing)
- Air Purifier Replacement: $100 – $1000+ (depending on the size and features)
FAQ Section
Q: Is any amount of ozone safe?
A: No. While the EPA has set a health advisory level for ozone, any exposure can cause irritation and health effects. It’s best to minimize ozone exposure as much as possible.
Q: Can I modify my air purifier to eliminate ozone production?
A: It’s generally not recommended to modify an air purifier yourself. This could void the warranty and potentially create a safety hazard.
Q: Are all ionizers bad?
A: Not necessarily. Some ionizers produce very low levels of ozone and are considered relatively safe. However, it’s best to choose a purifier that doesn’t rely on ionization as its primary cleaning method.
Q: How does the size of the room affect ozone concentration?
A: In a smaller room, ozone will concentrate more quickly than in a larger, well-ventilated space.
Alternative Solutions Section
If you’re concerned about ozone but still want the benefits of ionization, consider a purifier that uses bipolar ionization. This technology generates both positive and negative ions, which are thought to be less likely to produce ozone.
| Solution | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEPA/Carbon Filter | Safe, effective at removing particles & odors | Doesn’t address gases effectively | Most homes, allergy sufferers |
| Bipolar Ionization | Potentially lower ozone production | Newer technology, long-term effects unknown | Those seeking ionization benefits with reduced ozone risk |
Keep Your Air Running Smoothly
You now have the tools to identify and address potential ozone emissions from your air purifier. Remember to prioritize air purifiers with HEPA and carbon filters, disable ozone-generating features when possible, and regularly monitor your air quality. By taking these steps, you can enjoy cleaner, healthier air without compromising your well-being.
Have you tested your air purifier for ozone? Share your experience and any helpful tips in the comments below!